Strongswan Jumphost mit Mikrotik Client als Switch
Hallo zusammen,
ich habe mit der freundlichen Hilfe von aqui in diesem Beitrag:
dyndns-mit-ds-lite-fuer-l2tp-mit-mikrotik
eine Umgebung auf die Beine gestellt, mit der verschiedene FritzBoxen und ein MikroTik sich per ipsec auf einen vServer schalten.
Damit kann ich mich also von irgendeinem Endgerät aus mit dem VPN Server verbinden und dann auf die Netze der Fritzboxen/Mikrotik etc zugreifen.
Soweit so gut.
Wenn ich mich jetzt also mit meinem Rechner entsprechend mit dem vServer verbinde, hat dieser dann die öffentliche IP Adresse meines vServers. Meine Frage ist jetzt, kann ich auch zb einen Mikrotik als "Client" mit dem Server verbinden, sodass die Geräte die dann mit dem Mikrotik per zB Wlan verbunden sind auch mit dem vServer verbunden sind ?
Also quasi, der Mikrotik verbindet sich dem vServer und mein Iphone ist per Wlan mit dem Mikrotik verbunden und bekommt dann auch, statt der öffentlichen IP Adresse des uplinks des MT (79.x.x.x) die öffentliche IP Adresse des vServers (157.x.x.x)
Klar, das Iphone ist jetzt ein schlechtes Beispiel, hier könnte ich natürlich auch einfach die VPN Verbindung direkt auf dem Smartphone einrichten und das Iphone verbindet sich selbstständig mit dem vServer.
Aber es gibt ja auch durchaus Endgeräte die weniger Einstellungsmöglichkeiten oder Zertifikatsverwaltung haben.
Da wäre es halt Klasse wenn sich praktisch nur der MT per VPN verbinden müsste und dann quasi als Switch für alle anderen Geräte dient die an ihn angeschlossen sind.
Ich hoffe es ist verständlich worauf ich hinaus will, falls nicht, schiebe ich das einfach mal auf die Uhrzeit ^^
VG
ich habe mit der freundlichen Hilfe von aqui in diesem Beitrag:
dyndns-mit-ds-lite-fuer-l2tp-mit-mikrotik
eine Umgebung auf die Beine gestellt, mit der verschiedene FritzBoxen und ein MikroTik sich per ipsec auf einen vServer schalten.
Damit kann ich mich also von irgendeinem Endgerät aus mit dem VPN Server verbinden und dann auf die Netze der Fritzboxen/Mikrotik etc zugreifen.
Soweit so gut.
Wenn ich mich jetzt also mit meinem Rechner entsprechend mit dem vServer verbinde, hat dieser dann die öffentliche IP Adresse meines vServers. Meine Frage ist jetzt, kann ich auch zb einen Mikrotik als "Client" mit dem Server verbinden, sodass die Geräte die dann mit dem Mikrotik per zB Wlan verbunden sind auch mit dem vServer verbunden sind ?
Also quasi, der Mikrotik verbindet sich dem vServer und mein Iphone ist per Wlan mit dem Mikrotik verbunden und bekommt dann auch, statt der öffentlichen IP Adresse des uplinks des MT (79.x.x.x) die öffentliche IP Adresse des vServers (157.x.x.x)
Klar, das Iphone ist jetzt ein schlechtes Beispiel, hier könnte ich natürlich auch einfach die VPN Verbindung direkt auf dem Smartphone einrichten und das Iphone verbindet sich selbstständig mit dem vServer.
Aber es gibt ja auch durchaus Endgeräte die weniger Einstellungsmöglichkeiten oder Zertifikatsverwaltung haben.
Da wäre es halt Klasse wenn sich praktisch nur der MT per VPN verbinden müsste und dann quasi als Switch für alle anderen Geräte dient die an ihn angeschlossen sind.
Ich hoffe es ist verständlich worauf ich hinaus will, falls nicht, schiebe ich das einfach mal auf die Uhrzeit ^^
VG
Bitte markiere auch die Kommentare, die zur Lösung des Beitrags beigetragen haben
Content-ID: 8790082338
Url: https://administrator.de/forum/strongswan-jumphost-mit-mikrotik-client-als-switch-8790082338.html
Ausgedruckt am: 06.08.2025 um 04:08 Uhr
5 Kommentare
Neuester Kommentar
Aloha!
Ja das geht.
Also mit local_ts jegliche Zieladressen erlauben.
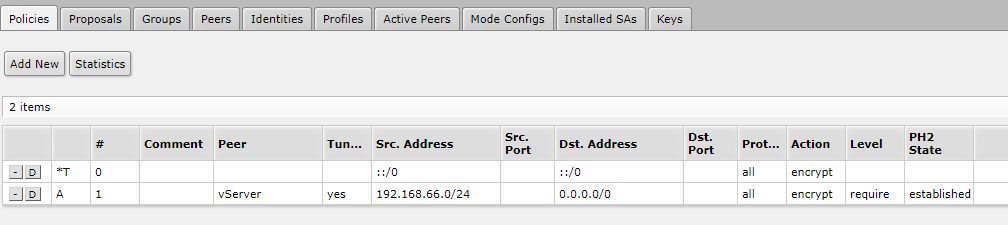
Die 192.168.88.0/24 natürlich an das Subnetz anpassen welches von deinem Mikrotik kommt und welches in der IPSec Policy am Mikrotik als SRC steht.
Noch als wichtiger Hinweis:
Bei Verwendung von 0.0.0.0/0 für das spezifizierte Subnetz geht wirklich alles über den Tunnel , auch Anfragen an andere lokale Netze die am Mikrotik an liegen. Das führt dazu dass diese anderen lokalen Netze dann nicht mehr von diesem Subnetz aus erreichbar sind.
Wenn du aus diesem Subnetz auch andere lokale Subnetze weiter erreichen können willst, dann musst du sogenannte Bypass Policies für jedes dieser lokalen Netze erstellen deren action auf "none" statt "encrypt" steht:
Im Beispiel wäre 192.168.99.0/24 ein anderes Netz das am Mikrotik angebunden wäre.
Wichtig ist das diese Policies vor der Policy stehen die 0.0.0.0/0 als dst-address definiert hat, denn auch hier gilt wie in der Firewall "first match wins".
Im Befehl bewirkt das "place-before=0" das diese Policy ganz oben in der Liste angelegt wird.
Diese Bypass Regeln sind nötig weil der IPSec-Encryption Prozess erst ganz zum Schluss nach der POSTROUTING Chain eingreift und dieser nur anhand der IPSec-Policies entscheided ob verschlüsselt wird oder nicht.
Pj
Ja das geht.
- Dazu in der IPSec Policy am Mikrotik die dst-address auf 0.0.0.0/0 stellen, damit erzwingst du das sämtlicher Traffic des Subnetzes welches in der Policy als src-address definiert ist über den Tunnel raus geht.
/ip ipsec policy add dst-address=0.0.0.0/0 level=unique peer=XXXXXXX proposal=XXXXXX src-address=192.168.88.0/24 tunnel=yes- In strongswan muss dann aber noch die Verbindung so angepasst werden
children {
net {
local_ts = 0.0.0.0/0
remote_ts = 192.168.88.0/24
esp_proposals = aes256-sha512-modp1024,aes256-sha1-modp1024
}
}Die 192.168.88.0/24 natürlich an das Subnetz anpassen welches von deinem Mikrotik kommt und welches in der IPSec Policy am Mikrotik als SRC steht.
- Dann noch in der Firewall des vServer das Forwarding für das 192.168.88.0/24 Subnetz erlauben und dieses Subnetz in der POSTROUTING Chain "masqueraden" damit es vom vServer aus ins Internet geNATet wird.
Noch als wichtiger Hinweis:
Bei Verwendung von 0.0.0.0/0 für das spezifizierte Subnetz geht wirklich alles über den Tunnel , auch Anfragen an andere lokale Netze die am Mikrotik an liegen. Das führt dazu dass diese anderen lokalen Netze dann nicht mehr von diesem Subnetz aus erreichbar sind.
Wenn du aus diesem Subnetz auch andere lokale Subnetze weiter erreichen können willst, dann musst du sogenannte Bypass Policies für jedes dieser lokalen Netze erstellen deren action auf "none" statt "encrypt" steht:
/ip ipsec policy add action=none dst-address=192.168.99.0/24 src-address=192.168.88.0/24 place-before=0Wichtig ist das diese Policies vor der Policy stehen die 0.0.0.0/0 als dst-address definiert hat, denn auch hier gilt wie in der Firewall "first match wins".
Im Befehl bewirkt das "place-before=0" das diese Policy ganz oben in der Liste angelegt wird.
Diese Bypass Regeln sind nötig weil der IPSec-Encryption Prozess erst ganz zum Schluss nach der POSTROUTING Chain eingreift und dieser nur anhand der IPSec-Policies entscheided ob verschlüsselt wird oder nicht.
Pj
An den DNS Server gedacht den du den Clients verteilst? Wenn der im lokalen Netz liegt fehlt die Bypass Rule. Und die Bypass Policies sehe ich auch nicht.Lies dir meinen Abschnitt oben nochmal in Ruhe durch bitte.
In der SRCNAT Chain für IPSec ein Accept auf dem Mikrotik angelegt?
Ein Export wäre sinnvolle, mir Bildchen sieht man zu wenig ....
In der SRCNAT Chain für IPSec ein Accept auf dem Mikrotik angelegt?
Ein Export wäre sinnvolle, mir Bildchen sieht man zu wenig ....