Packet flow from VLAN Host to www - how often routing decision is made?
Hi there,
it has been a while
I'm reviewing my firewall rules and have some hiccups grasping all again.
I asked myself quite a basic question but my mind was filled with other things, so I would like to have a second opinion on it.
How often will a package flow through this before it hits www (or my ISP) if I have VLANs and Bridge
If I combine
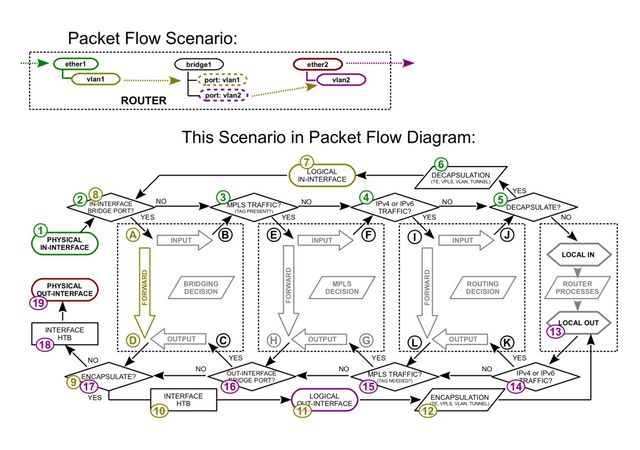
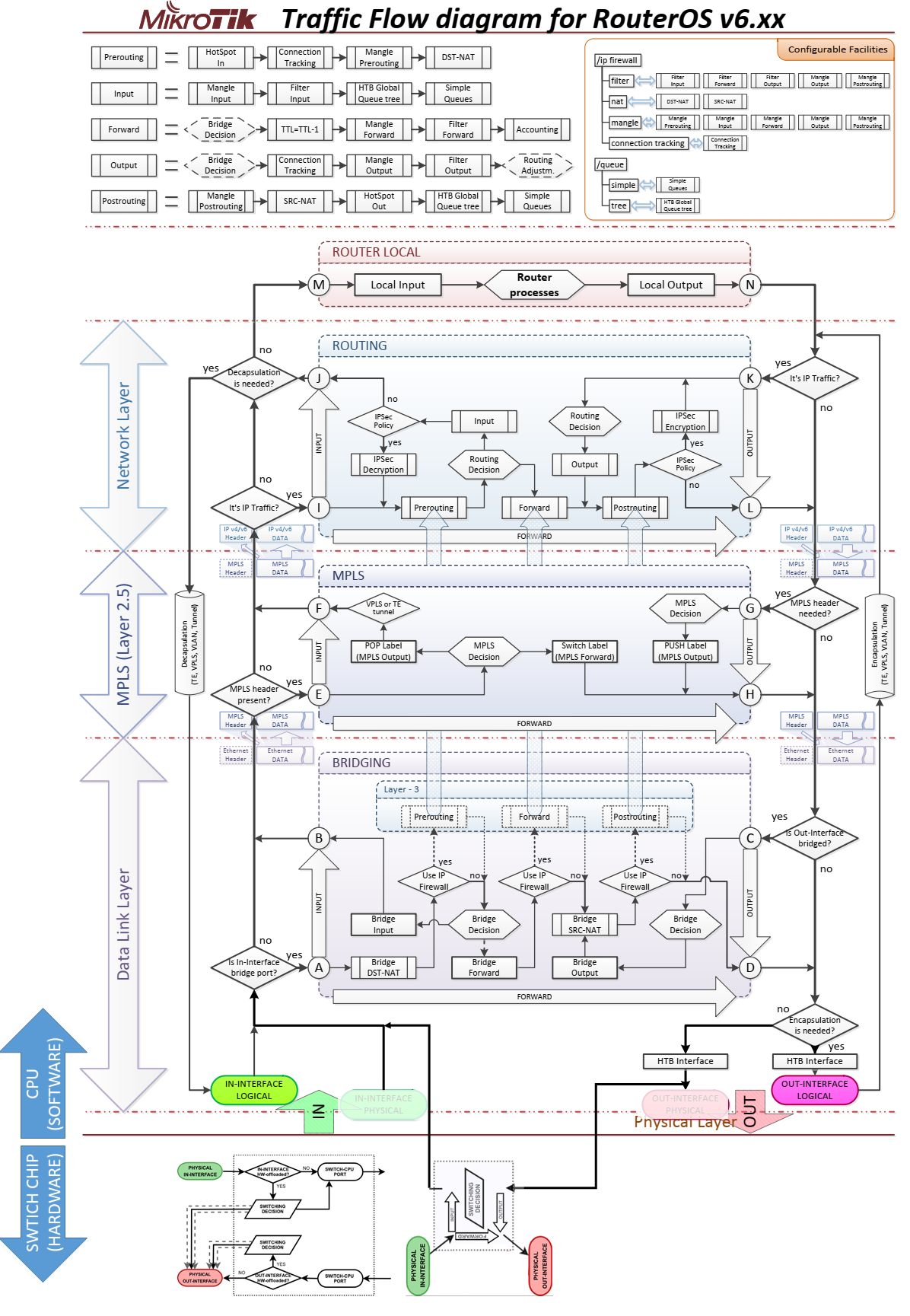
from Manual:Packet Flow - MikroTik Wiki | 4.3 Vlan Untagging/Tagging in the bridge interface and the Routing Packet Flow Diagram from firewall vs nat packet flow - MikroTik
it is only once, isn't it?
Simplified it is:
it has been a while
I'm reviewing my firewall rules and have some hiccups grasping all again.
I asked myself quite a basic question but my mind was filled with other things, so I would like to have a second opinion on it.
How often will a package flow through this before it hits www (or my ISP) if I have VLANs and Bridge
If I combine
from Manual:Packet Flow - MikroTik Wiki | 4.3 Vlan Untagging/Tagging in the bridge interface and the Routing Packet Flow Diagram from firewall vs nat packet flow - MikroTik
it is only once, isn't it?
Simplified it is:
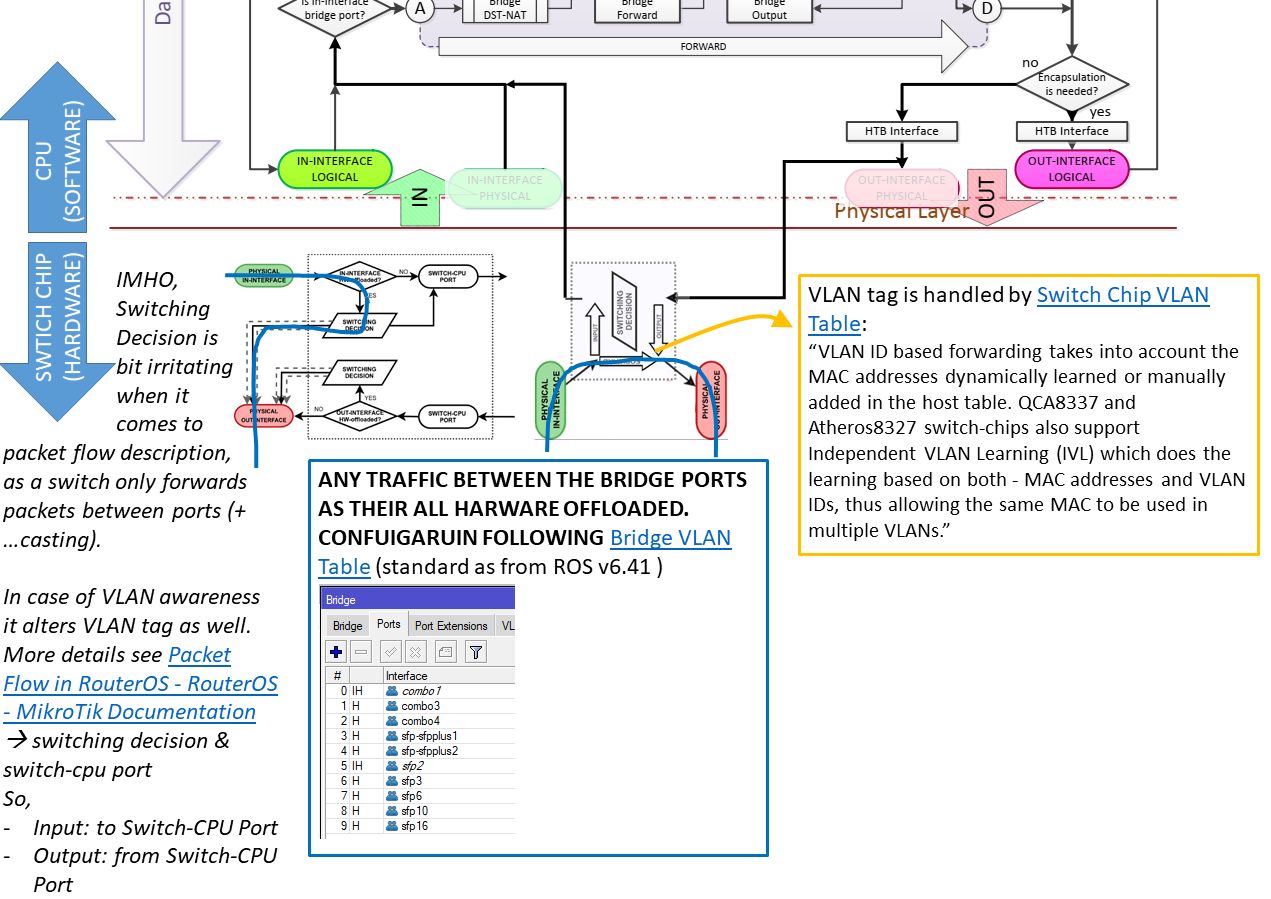
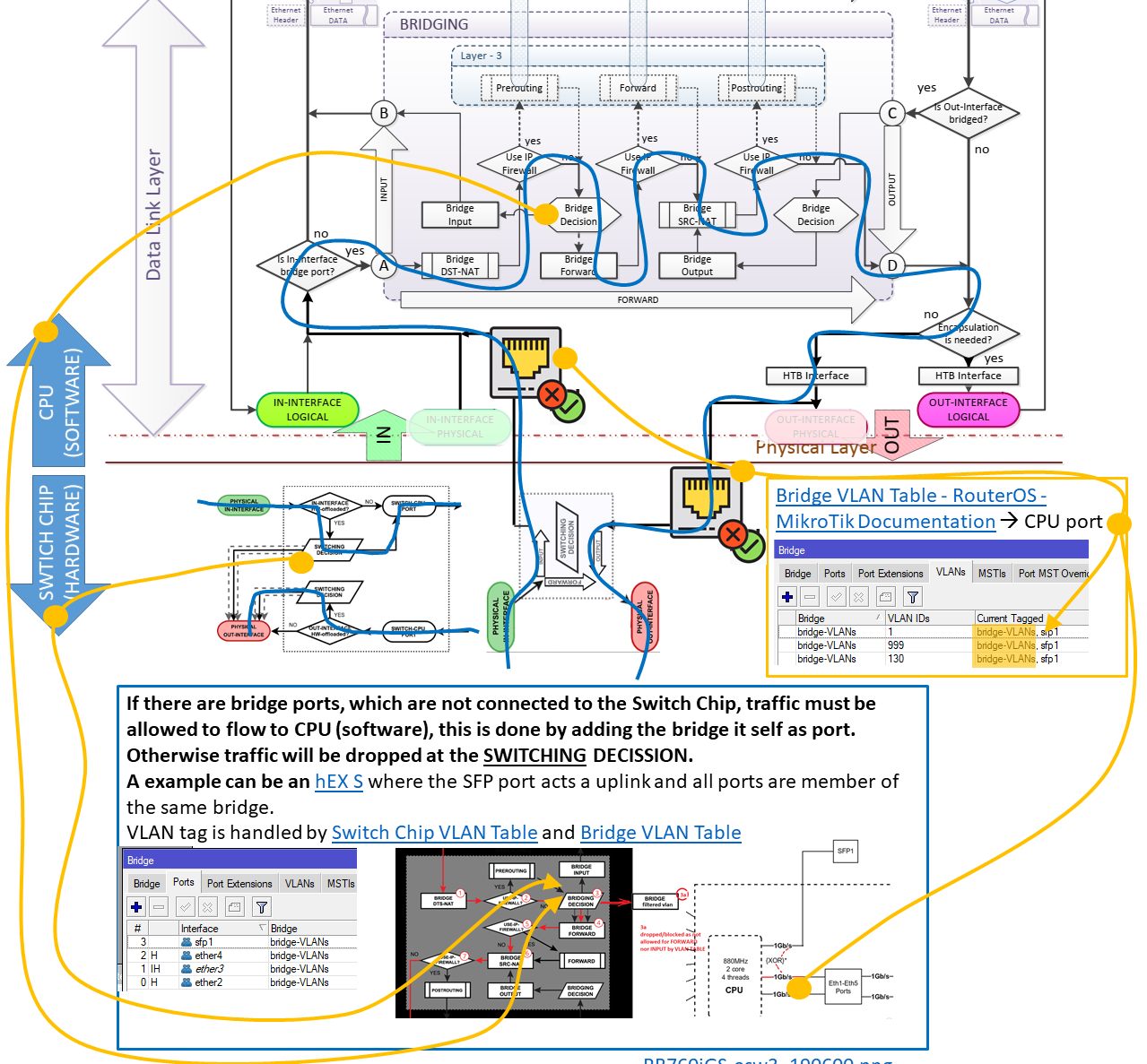
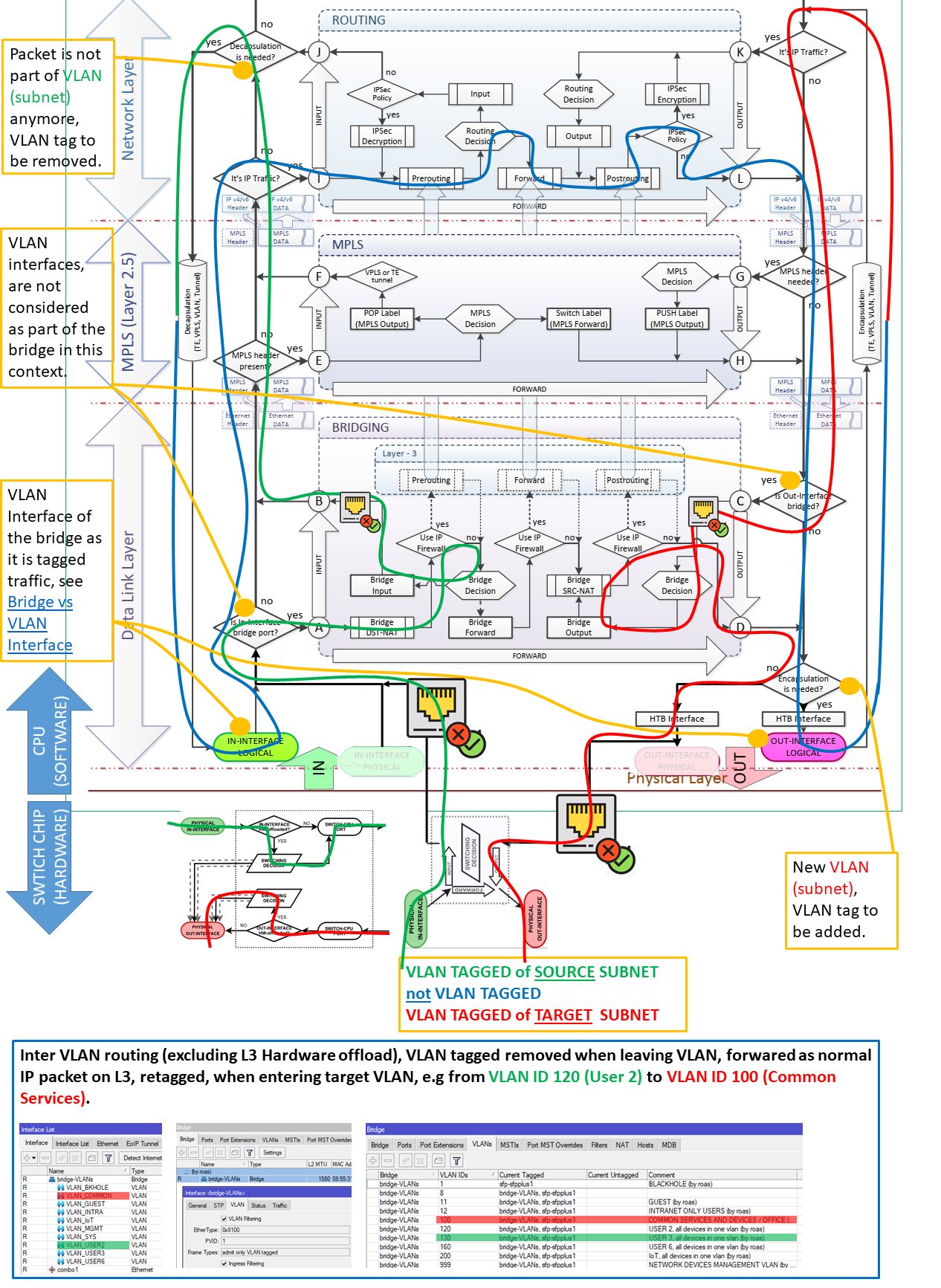
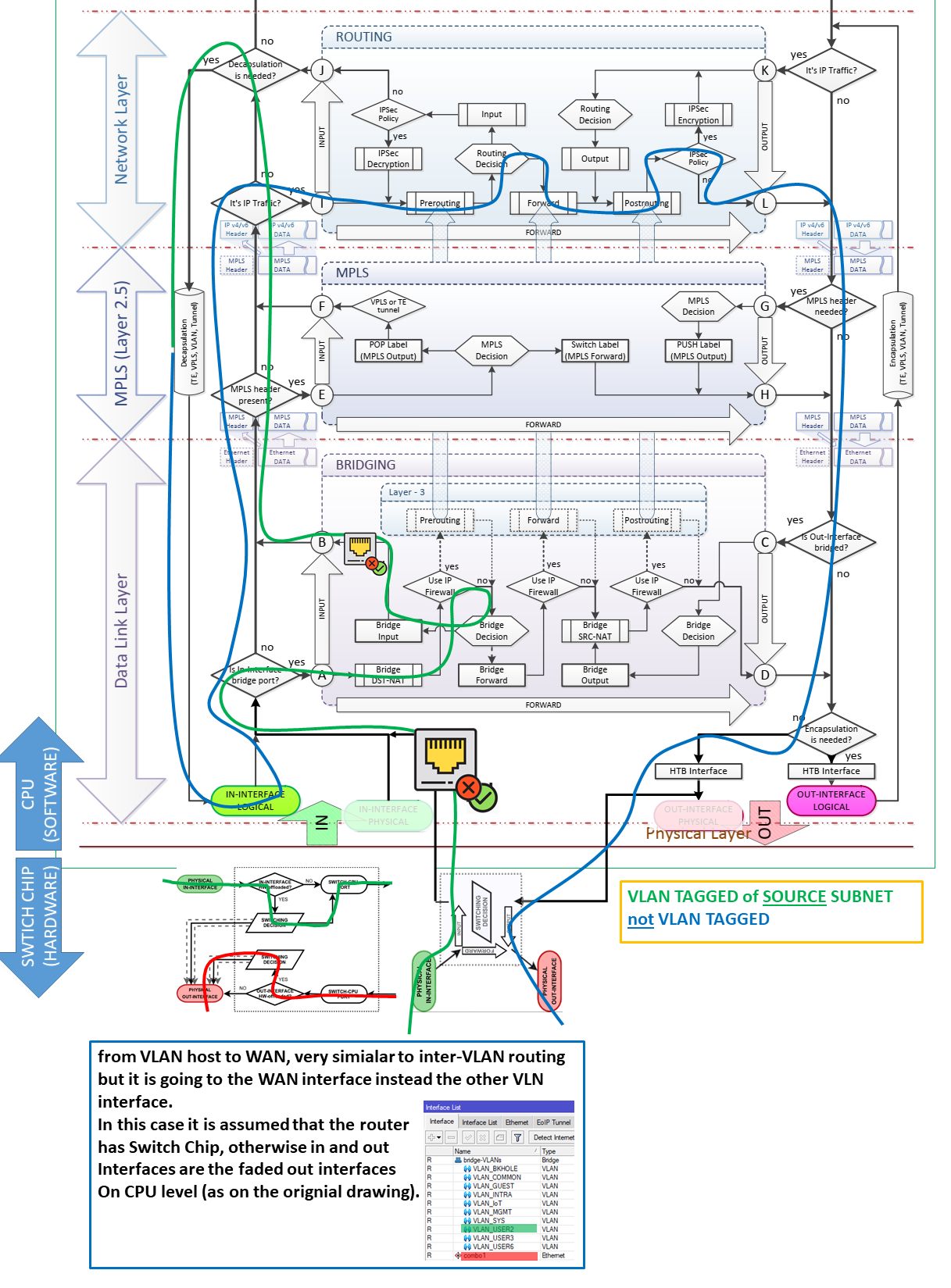
- From host to Interface on router (VLAN trunk / tagged port is the physical in)
- Then Decapsulation takes place
- Afterwards it goes to the Logical In Interface, the respective VLAN Interface
- Then, it is forwarded to the physical WAN interface where it leaves the router with any other processing on the router anymore
Bitte markiere auch die Kommentare, die zur Lösung des Beitrags beigetragen haben
Content-ID: 7151104211
Url: https://administrator.de/en/packet-flow-from-vlan-host-to-www-how-often-routing-decision-is-made-7151104211.html
Ausgedruckt am: 31.01.2025 um 02:01 Uhr
15 Kommentare
Neuester Kommentar
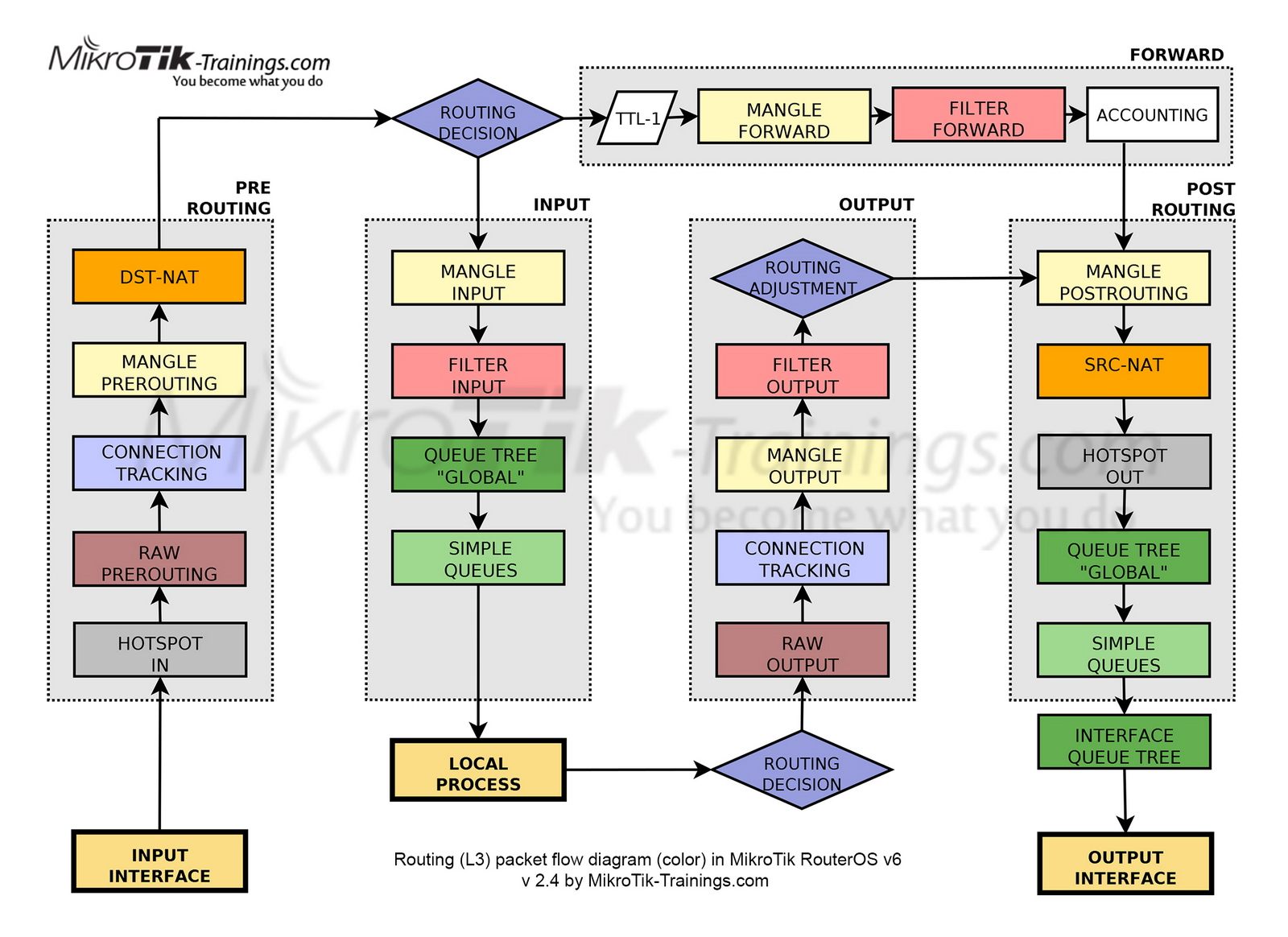
If it's a new paket wich cannot be matched by the connection tracking table then routing decision has to be made first, otherwise the packet belongs to an existing connection so it flows through the connection tracking process and is forwarded directly without further evaluation (excluding IPsec decapsualtion which has always to be done of course, also SRCNAT and DSTNAT have their own tables and processing takes place in PREROUTING(DSTNAT) and POSTROUTING(SRCNAT)).
This is called a statefull firewall. All modern firewalls use connection states, so you only have to define rules in one direction, the way back will then be allowed automatically by the connection tracking table.
With Mikrotik you have to setup a statefull firewall by your own rules! So you need to define at least two rules for INPUT and FORWARD chains wich have to evaluate the connection states "established,related, untracked" in their settings.
How long connections can stay open when there is no traffic for a period of time or the connection breaks unexpectedly without normal TCP FIN, can be defined in your firewall setup in the CONNTRACK table settings. Here you can define different settings for TCP, UDP, ICMP and so on.
Regards
This is called a statefull firewall. All modern firewalls use connection states, so you only have to define rules in one direction, the way back will then be allowed automatically by the connection tracking table.
With Mikrotik you have to setup a statefull firewall by your own rules! So you need to define at least two rules for INPUT and FORWARD chains wich have to evaluate the connection states "established,related, untracked" in their settings.
How long connections can stay open when there is no traffic for a period of time or the connection breaks unexpectedly without normal TCP FIN, can be defined in your firewall setup in the CONNTRACK table settings. Here you can define different settings for TCP, UDP, ICMP and so on.
Regards
Zitat von @PackElend:
How is the flow for the first package, the one with the state NEW?
As described in the OP?
How is the flow for the first package, the one with the state NEW?
As described in the OP?
It's going the "forward" path, because it's not a packet for the router itself ...
Zitat von @PackElend:
Before it hits the VLAN interface it is going to be decapsulated (VLAN tag removed)?
Before it hits the VLAN interface it is going to be decapsulated (VLAN tag removed)?
Yes.
Zitat von @PackElend:
Before it hits the VLAN interface it is going to be decapsulated (VLAN tag removed)?
Before it hits the VLAN interface it is going to be decapsulated (VLAN tag removed)?
Yes. The first image shows it clearly. Traffic is assigned to the logical interface inside
the router (vlanX) after decapsulation.
If that's all, please mark this thread as solved. Thanks.